Introduction to
Scientific Computing on a Cluster
Please navigate to
uiuc-cse.github.io/hpc-sp15
CSE Training • cse.illinois.edu/training/
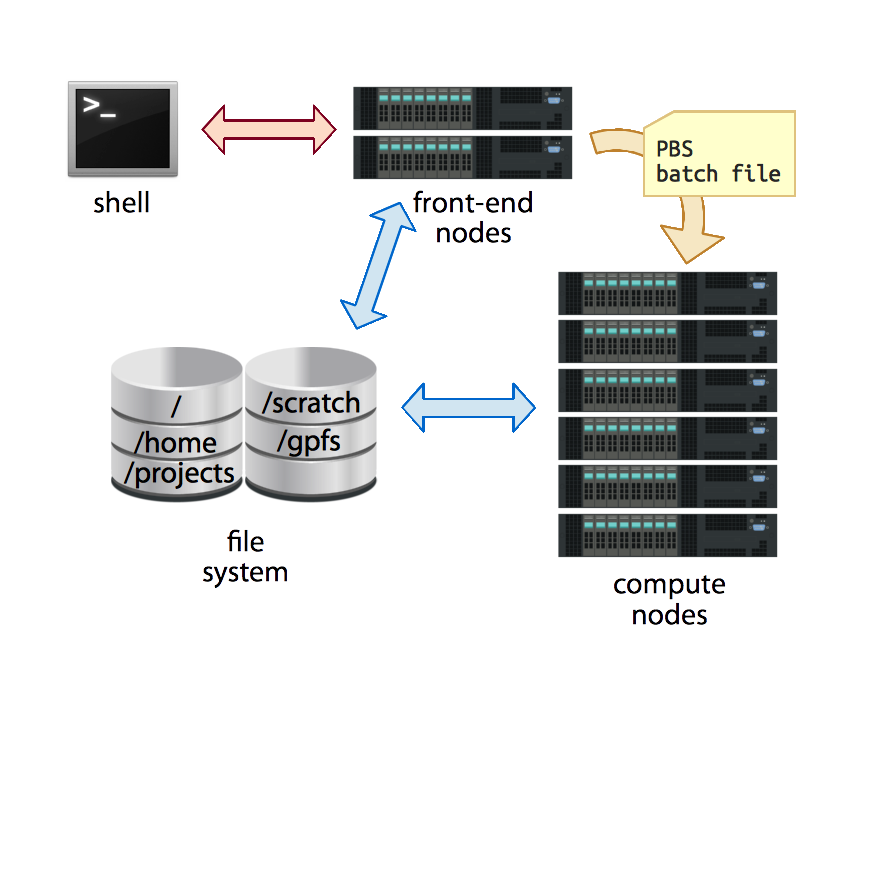
Cluster Elements
HPC Strategies
vectorization
single operation across multiple data
distributed computing
multiple units on multiple data for same overall process
local threading
context-switching processes operating over
multiple control flows or multiple data
HPC Architecture
GPGPU
“If you were plowing a field, which would you rather use?
Two strong oxen or 1024 chickens?”
(Seymour Cray)
Linked CPUs
HPC Performance
Speedup
how much faster a parallel algorithm is than its sequential counterpart
S(N, P)=tN,P=1 / tN,P
HPC Performance
Strong Scaling
how the solution time varies with the number of processors P for a fixed total problem size N.
E(N) = t1 / (N tN)
HPC Performance
Weak Scaling
how the solution time varies with the number of processors P for a fixed problem size per processor N/P.
E(N)
= (t1
/ tN)
Where can you go next?
http://hpcuniversity.org/roadmap/
Courses
-
ECE 408/CS 483 Applied Parallel Programming
-
ECE 492/CS 420/CSE 402 Introduction to Parallel Programming
-
ECE 428/CS 425/CSE 424 Distributed Systems
-
CS 524 Concurrent Programming Languages
-
CS 525 Advanced Topics in Distributed Systems
-
CS 533 Parallel Computer Architectures
-
CS 554/CSE 512 Parallel Numerical Algorithms
-
ECE 598HK/CS 598HK Many-Core Computing
MSE 498AF Computational Materials Science and Engineering
HPC-Sp15
By uiuc-cse
HPC-Sp15
- 764

